Indirect taxes are taxes that raise the price of a good so consumers essentially paying the tax during purchasing the goods; which mean paying more for the product. This main cause why consumers thought of as taxes that are passed on, as the price of the tax is salaried for by increasing the overall price of the goods or service. Fuel, alcohol and cigarettes taxes are all considered examples of indirect taxes, many have disagree that the tax is actually paid by the end consumer in a way of a higher retail price. An inefficient marketplace and alter market prices that doesn't match their equilibrium,
What happen if the government ignores the price floor?

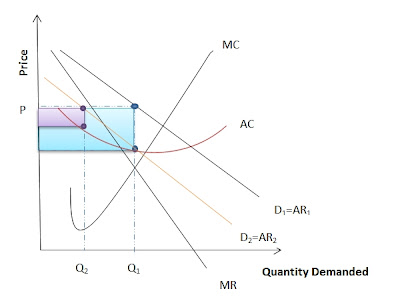
For government, the price floor is useful so that government can use as the medium to prevent consumer from buying certain goods; alcohol and cigarettes. Then government can occur on the market and set the minimum price on the goods to be sold at or above. By doing this, suppliers are forced to increase prices of their goods and as a result the quantity demanded decrease. To be effective, the price floor should be set above the market equilibrium. In another hand, from time to time there is an illegal market can be extend where the goods is sold at the original market price. For example, in other country; United Kingdom it is not infrequent to find small dealers that illegally import large stocks of cigarettes and sell them for about half the price of cigarettes that can be bought in shops. This can repeatedly make a political party not been accepted with the large powerful firms and this can affect their future political success especially in US.

Why does government apply tax on alcohol and cigarettes?
Government applies tax on alcohol and cigarettes to increases the government revenue as elasticity for these items is inelastic. Since most of the people are habitual alcoholics and smokers and when they are addicted to these things, they are willing to pay a hefty price just to get it.
The imposition of either type of indirect tax has an effect similar to a rise in production costs. This means that a firm's supply curve will shift up vertically by the amount of the tax. This can be shown in the graph below by a unit tax that will shift the supply curve by the full amount of the tax, so the new curve is parallel to the original .
Does the price elasticity of demand effected?
In majority cases, the burden is split between producers and consumers are worse off. With indirect tax, suppliers or producers may be able to pass on some or all the indirect taxes onto consumer through higher prices. The tax and the ability of businesses depends on the price elasticity of demand supply carries that is known as shifting the burden. In the diagram shows that the rate on the consumer is indicated by the price rise, P to P1, and times the new quantity sold, 0 to Q1.The vertical distance is the tax per unit which is greater than the price rise , therefore the rate on the producer is measured as the distance P to X, times 0 to Q1;the green shaded area. The exact division depends upon how consumer react to price rise which is their price elasticity of demand.
The differences when demand is price elastic or inelastic
References: